How the Instrumental Physiotherapy is performed
The instrumental physiotherapy treatments need the doctor’s prescription and are performed by qualified personnel in possession of a Physiotherapy Diploma.
Each treatment can be used for osteo-muscle-tendon pathologies and/or joint deficits. Generally, they are aimed at low back disorders such as sciatica, crural pain or general back pain. They can also be used for cervical pain, scapulohumeral periarthritis, gonarthrosis, rhizarthrosis, etc. More than one treatment can be applied during the day, even sequentially. However, according to the evolutionary moment of the symptomatology, the doctor decides which is the most appropriate type of electro- medical treatment such as Electroanalgesia, Tecar, ultrasound, etc. Instrumental physiotherapy is the branch of rehabilitation medicine that uses physical energies for therapeutic purposes. The impact of these energies on tissues generates a chain of biological reactions that have specific therapeutic effects such as: analgesia, activation of the local metabolism, muscle contraction or toning, etc.
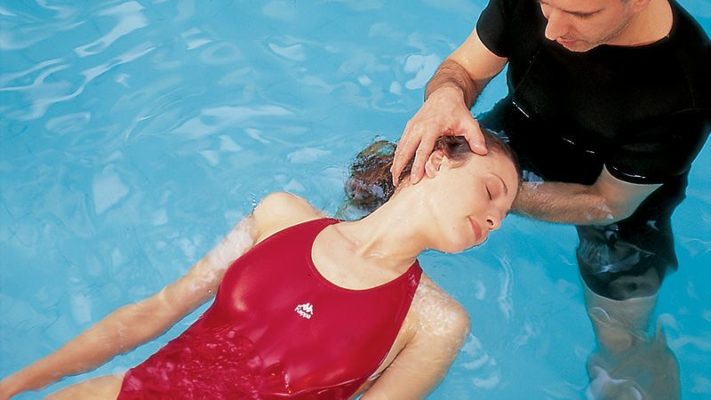
The instrumental physiotherapy can be assisted by manual physiotherapy in the gym or by Leopoldina thermal water in the rehabilitation courses in the thermal pool.
Diadynamics: antalgic electrotherapy; it uses low frequency current, useful in pain therapy.
Hydrogalvanic: continuous electrical current in water, trophic and analgesic effect on tissues.
Iontophoresis: electrotherapeutic technique which allows the transport of a medicine through the epidermis for anti- inflammatory and analgesic purposes.
Paraffin therapy: it belongs to thermotherapy. Useful for articular arthrosis (hands and feet), based on the characteristics of this substance.
Tens: electrotherapy technique with analgesic activity.
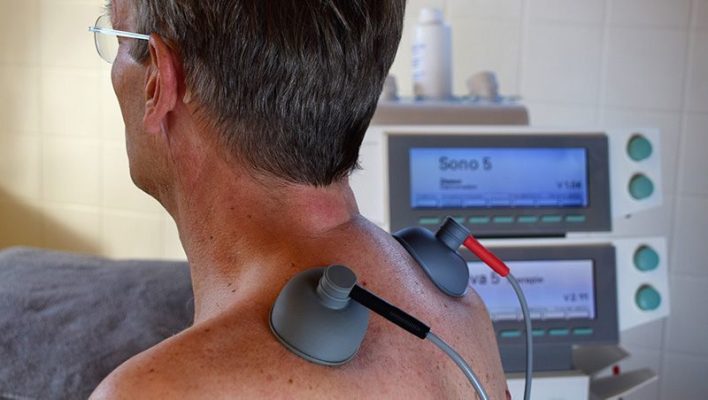
Ultrasound: acoustic vibrations that generate high intensity micromassages on deep tissues with mechanical and thermotherapeutic effect.
Magnetotherapy: physical therapy that uses magnetic fields. Useful for osteoporosis and in calcification delays.
Electrostimulation: therapeutic rehabilitation practice for the functional recovery of atrophic muscle masses.
Laser therapy: Electromagnetic radiation capable of intervening on muscle-tendon and joint inflammation.
Tecartherapy: cellular energetic activation with anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving activity of osteoarticular and muscular, acute and chronic pathologies.
Consult the “SCIENTIFIC MANUAL”